Benchmarking android with workload automation
What is wa
Workload Automation (WA) is a framework for executing workloads and collecting measurements on Android and Linux devices. WA includes automation for nearly 40 workloads and supports some common instrumentation (ftrace, hwmon) along with a number of output formats.
WA is heavily depend on devlib, which was also created by ARM and under active development.
Installation
Install wlauto
To avoid install failure, it is recommended that you update pip and setuptools before proceding with installation:
pip install --upgrade --user pip
pip install --upgrade --user setuptools
Now, install workload-automation with:
pip install --user wlauto
Alternatively, you may wanna install latest development version from github:
git clone https://github.com/ARM-software/workload-automation.git
pip install --user ./workload-automation
Install Android SDK
To use wa, Android SDK is required to be installed and properly setup, download SDK tools package from sdk-tools-linux-4333796.zip and setup ANDROID_HOME:
export ANDROID_HOME=/opt/android-sdk/
Run a simple workload
In order to run workload we need to know what workloads wa supports, wa list workloads will show all the workloads currently supported by wa.
wa has a default config file under $HOME/.workload_automation/, named config.yaml
As we will run workloads on Android devices, additional configuration needs to be added to this file:
device_config:
device: 192.168.123.15:5555
working_directory: '/data/local'
load_default_modules: false
The last two lines are optional.
If you don’t wanna bother with default config file, you can also specify ip address in agenda, go to next section for example.
Now, do ‘wa run dhrystone’ will make wa run workload dhrystone with the default configuration with addtions for android devices. wa_output contains all results of this run.
Agenda
Running a single workload is easy, and normally of little use, what if I wanna run several workloads, what if I wanna setup android devices in boost mood.
To do complicated jobs, we need to create an “agenda”, to get an general idea what aganda looks like, see lisa agenda examples.
Creating a workload
In this section we will create a workload for doing some arithmetics using android calculator, as this process involving digit selection, we will create a apkuiauto type of workload:
fdbai@fdbai-desktop:/tmp$ wa create workload -k apkuiauto calculator
We can find the newly created workload in $HOME/.workload_automation/plugins/calculator.
The directory structure looks like this:
.
|-- __init__.py
`-- uiauto
|-- app
| |-- build.gradle
| `-- src
| `-- main
| |-- AndroidManifest.xml
| `-- java
| `-- com
| `-- arm
| `-- wa
| `-- uiauto
| `-- UiAutomation.java
|-- build.gradle
|-- build.sh
|-- gradle
| `-- wrapper
| |-- gradle-wrapper.jar
| `-- gradle-wrapper.properties
|-- gradlew
|-- gradlew.bat
`-- settings.gradle
For more options on creating workload, issue below command for more:
$ wa create workload -h
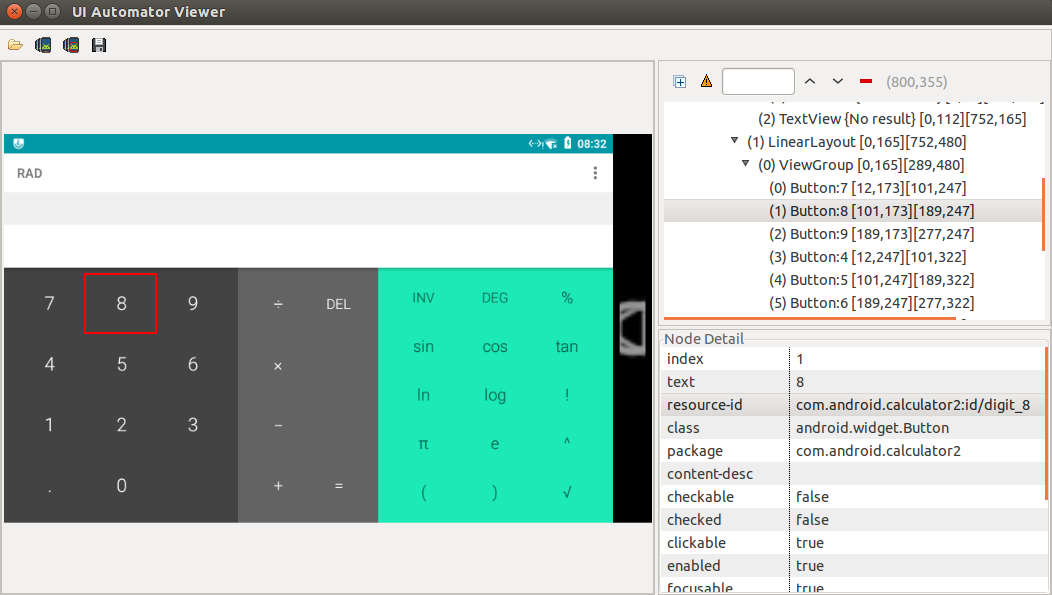
uiautomatorviewer
UI object can be inspected with uiautomatorviewer:
- Go to $ANDROID_HOME/tools/bin/
- execute ./uiautomatorviewer
- click the second button from left side
- wait for hierarchy to be displayed
- click the desired element, you’ll see the node detail in the right panel
The following changes are what we made to make workload calculator to work:
diff --git a/__init__.py b/__init__.py
index 32123c0..ab98f03 100644
--- a/__init__.py
+++ b/__init__.py
@@ -6,12 +6,12 @@ class Calculator(ApkUiautoWorkload):
name = 'calculator'
description = "This is an placeholder description"
# Replace with a list of supported package names in the APK file(s).
- package_names = ['package_name']
+ package_names = ['com.android.calculator2']
parameters = [
# Workload parameters go here e.g.
Parameter('example_parameter', kind=int, allowed_values=[1,2,3],
- default=1, override=True, mandatory=False,
+ default=1, override=False, mandatory=False,
description='This is an example parameter')
]
diff --git a/uiauto/app/src/main/java/com/arm/wa/uiauto/UiAutomation.java b/uiauto/app/src/main/java/com/arm/wa/uiauto/UiAut
index 14cc13b..87461f6 100644
--- a/uiauto/app/src/main/java/com/arm/wa/uiauto/UiAutomation.java
+++ b/uiauto/app/src/main/java/com/arm/wa/uiauto/UiAutomation.java
@@ -46,7 +46,16 @@ public class UiAutomation extends BaseUiAutomation {
@Test
public void runWorkload() throws Exception {
- // The main UI Automation code goes here
+ // The main UI Automation code goes here
+ UiObject digit =
+ mDevice.findObject(new UiSelector().resourceId(packageID + "digit_8"));
+ digit.click();
+ UiObject op = mDevice.findObject(new UiSelector().resourceId(packageID + "op_add"));
+ op.click();
+ digit = mDevice.findObject(new UiSelector().resourceId(packageID + "digit_9"));
+ digit.click();
+ UiObject result = mDevice.findObject(new UiSelector().resourceId(packageID + "eq"));
+ result.click();
}
After this, go to uiauto directory, execute ./build.sh and wait for build complete.
Run directly with ‘wa run calculator -vf’ or create an agenda like this:
fdbai@fdbai-desktop:~/perf/wa/calculator$ cat calc.yaml
config:
iterations: 10
max_retries: 5
execution_order: by_workload
device: generic_android
device_config:
device: 192.168.123.15:5555
workloads:
- name: calculator
Now, run wa run calc.yaml -vf to see what happens.
applaunch
This workload launches and measures the launch time of applications for supporting
workloads which implement ApplaunchInterface.
To support applaunch, workload should override the following abstract methods:
- runApplicationSetup
- getLaunchEndObject
- getLaunchCommand
- setWorkloadParameters
Take the workload calculator for example:
diff --git a/uiauto/app/src/main/java/com/arm/wa/uiauto/UiAutomation.java b/uiauto/app/src/main/java/com/arm/wa/uiauto/UiAut
index 87461f6..f3199cf 100644
--- a/uiauto/app/src/main/java/com/arm/wa/uiauto/UiAutomation.java
+++ b/uiauto/app/src/main/java/com/arm/wa/uiauto/UiAutomation.java
@@ -19,10 +19,13 @@ import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
+import com.arm.wa.uiauto.ApplaunchInterface;
import com.arm.wa.uiauto.BaseUiAutomation;
+import com.arm.wa.uiauto.ActionLogger;
+import com.arm.wa.uiauto.UiAutoUtils;
@RunWith(AndroidJUnit4.class)
-public class UiAutomation extends BaseUiAutomation {
+public class UiAutomation extends BaseUiAutomation implements ApplaunchInterface {
protected Bundle parameters;
protected String packageID;
@@ -67,4 +70,29 @@ public class UiAutomation extends BaseUiAutomation {
public void teardown() throws Exception {
// Optional: Perform any clean up for the workload
}
+
+ public void runApplicationSetup() throws Exception {
+ // do nothing;
+ }
+
+ // Sets the UiObject that marks the end of the application launch.
+ public UiObject getLaunchEndObject() {
+ UiObject launchEndObject =
+ mDevice.findObject(new UiSelector().resourceId(packageID + "digit_8")
+ .className("android.widget.Button"));
+ return launchEndObject;
+ }
+
+ // Returns the launch command for the application.
+ public String getLaunchCommand() {
+ String launch_command;
+ launch_command = UiAutoUtils.createLaunchCommand(parameters);
+ return launch_command;
+ }
+
+ // Pass the workload parameters, used for applaunch
+ public void setWorkloadParameters(Bundle workload_parameters) {
+ parameters = workload_parameters;
+ packageID = getPackageID(parameters);
+ }
}
Run applaunch with this agenda:
config:
iterations: 10
max_retries: 5
execution_order: by_workload
device: generic_android
augmentations: [uxperf]
workloads:
- name: applaunch
id: applaunch
workload_parameters:
workload_name: 'calculator'
applaunch_iterations: 5
markers_enabled: True
NOTE: markers_enabled must be set to True to make uxperf working.
